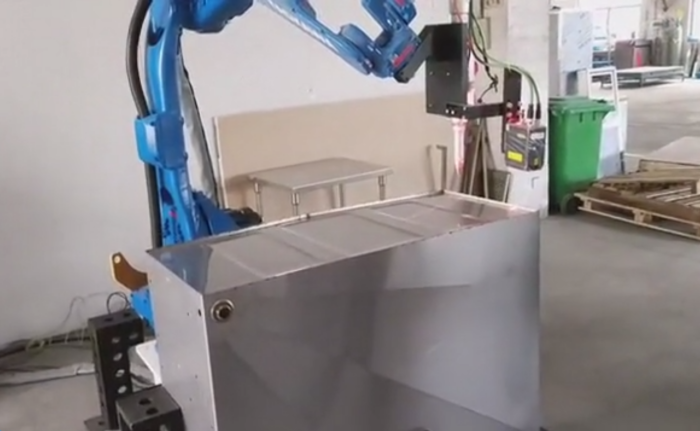
What is Robot Welding ?
According to a Business Wire report, by 2026, the robotic welding market is projected to nearly double from a 2018 value of $5,450.5 million to $10,784.4 million.
There are a number of key drivers behind the expansion of robotic welding. First and foremost, industrialization is growing at a rapid pace throughout the world, especially the automotive and metal industries. There is also an increase in customer demands, and many manufacturers can’t keep up.
Robotic welding assists both manufacturers and the customer in creating more efficient processes. On the supply chain, robotic welding provides the following advantages:
- Increased speed and improved accuracy of operations in warehousing and manufacturing
- Improved efficiency through robot and human collaborative working
- Reduced risk of employee injury
Automation is the way of the supply chain future. It decreases long-term costs, provides labor and machinery utilization stability, increases productivity, reduces error rates and frequency of inventory checks, and optimizes the component picking and sorting process.
With robotic welding, OEM suppliers move seamlessly into the future. In this article, we provide a brief overview of how robotic welding works, its advantages over manual welding and the most common robotic welding processes.
What Is Robotic Welding?
Robotic welding is a manufacturing process that uses mechanized programmable tools — which are also considered robots — for a completely automated welding process in which both the welding and the handling of the part are conducted by the robot. Typically, loading the ingot into the furnace is the only human involvement in the process.
Robotic welding has become increasingly more popular because of its mostly human-independent process. The most commonplace robotic welding machinery is made up by two main components:
- The mechanical unit creates manipulations in the material or parts to create the component or product.
- The controller is considered the unit’s “brain” in that it is what makes the arms of the unit move based on a design implemented into the system.
- The movements of the unit can either be pre-programmed or guided by machine vision, which is an imaging-based automatic inspection and analysis technology.
Laser Welding uses a laser generator that delivers a laser light via a fiber optic cable through a robotic cutting head to weld pieces together. Laser welding is often used in high volume applications that require high accuracy, especially in the automotive sector.
Here are a few more advantages:
Faster, more consistent cycle times. Robotic welding systems can produce 24 hours a day, allowing for greater productivity and throughput.
Higher quality and higher volume. Welding at a high volume, systems can produce high-quality welds with speed, precision and efficiency to produce a high volume of diverse parts.
Fewer interruptions. Robotic welding systems allow for fewer interruptions caused by human-led manufacturing. This also creates a safer working environment and solves potential labor shortages.
Ultimately, manual welding can come with a lot of hidden costs and require the human welder to undergo training that takes time, skill and concentration to master the craft. Robotic welding, by contrast, produces components in a short amount of time with high precision and comes with fewer costs.